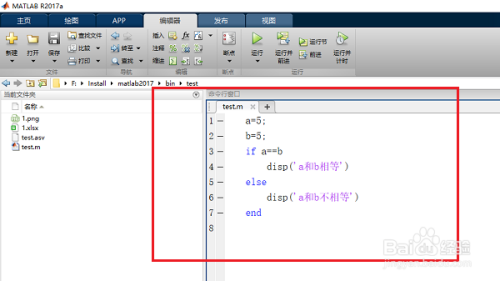
在MATLAB编程中,if语句是实现条件控制的基础结构,它允许程序根据特定条件执行不同的代码块。本文将详细介绍if语句的基本语法、高级用法以及实际应用示例。
一、if语句的基本语法
if语句的基本结构如下:
if condition
% 当条件为真时执行的代码
end其中,condition是一个逻辑表达式,当其结果为true(或非零值)时,执行if和end之间的代码。
示例:`matlab
x = 10;
if x > 5
disp('x大于5');
end`
二、if-else语句
当需要处理两种可能情况时,可以使用if-else结构:
if condition
% 条件为真时执行的代码
else
% 条件为假时执行的代码
end示例:`matlab
score = 75;
if score >= 60
disp('及格');
else
disp('不及格');
end`
三、if-elseif-else语句
对于多个条件判断,可以使用if-elseif-else结构:
if condition1
% 条件1为真时执行的代码
elseif condition2
% 条件2为真时执行的代码
elseif condition3
% 条件3为真时执行的代码
else
% 所有条件都为假时执行的代码
end示例:`matlab
temperature = 25;
if temperature > 30
disp('天气炎热');
elseif temperature > 20
disp('天气温暖');
elseif temperature > 10
disp('天气凉爽');
else
disp('天气寒冷');
end`
四、嵌套if语句
if语句可以嵌套使用,实现更复杂的条件判断:
if condition1
if condition2
% 条件1和条件2都为真时执行的代码
else
% 条件1为真但条件2为假时执行的代码
end
else
% 条件1为假时执行的代码
end五、逻辑运算符在if语句中的应用
MATLAB支持多种逻辑运算符,可以在if条件中组合使用:
&&:逻辑与(短路运算)||:逻辑或(短路运算)&:元素逻辑与|:元素逻辑或~:逻辑非
示例:`matlab
x = 10;
y = 5;
if x > 5 && y < 10
disp('两个条件都满足');
end`
六、向量化条件判断
MATLAB支持向量化操作,可以直接对数组进行条件判断:
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
B = A > 3; % 返回逻辑数组 [0, 0, 0, 1, 1]七、实用技巧和注意事项
- 使用缩进提高代码可读性
- 避免过多的嵌套,考虑使用switch语句或函数重构
- 注意浮点数比较的精度问题
- 使用
isequal函数比较数组
八、实际应用示例
示例1:求解二次方程`matlab
a = 1; b = -3; c = 2;
discriminant = b^2 - 4ac;
if discriminant > 0
x1 = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / (2a);
x2 = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2a);
fprintf('两个实根: x1 = %.2f, x2 = %.2f\n', x1, x2);
elseif discriminant == 0
x = -b / (2a);
fprintf('一个实根: x = %.2f\n', x);
else
realPart = -b / (2a);
imagPart = sqrt(-discriminant) / (2*a);
fprintf('两个复根: x1 = %.2f + %.2fi, x2 = %.2f - %.2fi\n', ...
realPart, imagPart, realPart, imagPart);
end`
示例2:成绩等级评定`matlab
score = input('请输入成绩: ');
if score >= 90
grade = 'A';
elseif score >= 80
grade = 'B';
elseif score >= 70
grade = 'C';
elseif score >= 60
grade = 'D';
else
grade = 'F';
end
fprintf('成绩等级: %s\n', grade);`
通过掌握if语句的各种用法,您可以在MATLAB中实现复杂的条件逻辑,编写更加灵活和强大的程序。建议多加练习,熟悉不同场景下的应用,提高编程效率。